Where Can International Students Study for Free in 2025?

For international students, the dream of studying abroad can often be overshadowed by daunting tuition fees. However, the pursuit of higher education without financial burden is not an impossible feat. Several countries offer tuition-free or very low-cost education to international students, making it a viable option for those seeking quality education on a budget. As we look ahead to 2025, this article delves into the specific destinations where international students can potentially study for free or at minimal cost. We will explore the eligibility criteria, available programs, and essential tips for navigating the application process, empowering aspiring scholars to make informed decisions and embark on their academic journey without the weight of excessive tuition fees.
Where Can International Students Study for Free in 2025?
Many international students dream of pursuing higher education abroad, but the cost can be a significant barrier. While completely free tuition is rare, several countries offer tuition-free or very low-cost options for international students, often at public universities. The availability and eligibility requirements for these programs can change, so it's crucial to stay updated. Here's a look at some possibilities for 2025.
Norway
Norway stands out as a prime destination. Public universities in Norway do not charge tuition fees to all students, regardless of their nationality. This applies to Bachelor's, Master's, and Ph.D. levels. However, students are typically required to pay a small semester fee (approximately 30-60 EUR) to the student welfare organization, which covers services like counseling, sports facilities, and health services. Keep in mind that the cost of living in Norway can be high, and proving sufficient funds for living expenses is a requirement for obtaining a student visa.
Germany
Germany is another attractive option. Public universities in most German states do not charge tuition fees for undergraduate and consecutive Master's programs to all students, including international students. However, some states might introduce or reintroduce tuition fees in the future, so it's crucial to check the specific regulations of the state where the university is located. Similar to Norway, a semester fee (usually around 150-300 EUR) is typically required, which covers public transportation and other student services.
Finland
Finland's situation is slightly different. While tuition fees are not charged to students pursuing studies in Finnish or Swedish, non-EU/EEA students are generally required to pay tuition fees for programs offered in English at the Bachelor's and Master's levels. However, doctoral studies remain free for all nationalities. There are also scholarship opportunities available to help cover tuition fees and living expenses.
Sweden
Like Finland, Sweden charges tuition fees to students from outside the EU/EEA and Switzerland for Bachelor's and Master's level programs. However, doctoral studies are generally free for all students. Swedish universities offer various scholarships to attract talented international students, so exploring these options is highly recommended.
Iceland
Public universities in Iceland do not charge tuition fees, but students are required to pay a registration fee (usually a few hundred USD) each academic year. While this fee is relatively low compared to tuition fees in other countries, it's important to factor in the high cost of living in Iceland.
| Country | Tuition Fees for International Students (2025 - Estimated) | Language of Instruction | Important Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Norway | Tuition-free at public universities (semester fee applies) | Norwegian, English (certain programs) | High cost of living. |
| Germany | Tuition-free at public universities in many states (semester fee applies) | German, English (certain programs) | Check state-specific regulations. |
| Finland | Tuition-free for programs in Finnish/Swedish and doctoral studies. Fees for non-EU/EEA students in English programs. | Finnish, Swedish, English | Scholarships available. |
| Sweden | Fees for non-EU/EEA/Swiss students in Bachelor's/Master's programs. Doctoral studies generally free. | Swedish, English (certain programs) | Scholarships available. |
| Iceland | Tuition-free (registration fee applies) | Icelandic, English (certain programs) | High cost of living. |
Which country is best for international students to study for free?
Tuition-Free Education in Germany
Germany is often cited as a top destination for free higher education. Many public universities in Germany do not charge tuition fees to undergraduate and doctoral students, regardless of their nationality. However, students are usually required to pay a semester contribution (Semesterbeitrag), which covers administrative costs, student services, and often includes a public transportation ticket. This contribution is significantly lower than tuition fees in many other countries. Opportunities for non-EU/EEA students may exist through scholarships and other funded programs.
- Public universities offer a wide range of programs in English and German.
- The semester contribution is mandatory but relatively low.
- Living costs in Germany can vary depending on the city.
Norway: A Nordic Option for Free Studies
Norway is another country known for its tuition-free higher education policy. Public universities in Norway do not charge tuition fees for all students, regardless of their nationality, for most undergraduate and graduate programs. As with Germany, students are required to pay a semester fee, but this is relatively low. However, keep in mind that the cost of living in Norway is quite high.
- Tuition is free at public universities for all students.
- The cost of living is considerably higher than in many other European countries.
- Certain specialized programs might have fees, so research is crucial.
Limited Tuition Fees in Austria
Austria offers relatively low tuition fees compared to many other Western countries. EU/EEA students generally pay a small semester fee, while non-EU/EEA students pay a significantly lower tuition fee than in many other countries. While not entirely tuition-free, the cost of studying in Austria is still considerably lower than in the United States or the United Kingdom. Scholarship options are available for students seeking financial aid.
- Tuition fees are significantly lower than in many other countries.
- EU/EEA students pay a smaller semester fee.
- Living costs are reasonable, especially compared to other Western European countries.
Finland: Exploring Free Education Opportunities
Finland has undergone changes in its tuition policies. While tuition fees are generally charged for non-EU/EEA students studying in English-taught bachelor's and master's programs, some opportunities for free education may still exist. Doctoral programs are often tuition-free for all students. It's essential to research specific programs and scholarships carefully to determine eligibility.
- Doctoral programs are often tuition-free.
- Scholarship opportunities can reduce or eliminate tuition fees for non-EU/EEA students.
- The Finnish education system is highly regarded.
Sweden: Focusing on Doctoral Studies
Similar to Finland, Sweden has introduced tuition fees for students from outside the EU/EEA. However, doctoral studies are generally tuition-free for all students. Students must research specific programs and explore available scholarships to reduce the cost of studying in Sweden. Keep in mind that the cost of living in Sweden is relatively high.
- Doctoral studies are generally tuition-free for all students.
- Scholarship opportunities are available for master's and bachelor's programs.
- Sweden is known for its research-intensive environment.
How can international students study in the US for free?

Merit-Based Scholarships
Many US universities offer merit-based scholarships to attract talented international students. These scholarships are awarded based on academic excellence, leadership skills, and other achievements. To maximize your chances:
- Research universities thoroughly: Identify institutions known for their strong academic programs and generous scholarship offerings for international students in your field of study.
- Maintain an excellent academic record: A high GPA and strong standardized test scores (like the TOEFL or IELTS and, if required, the GRE or GMAT) are crucial for competitiveness.
- Highlight extracurricular activities: Showcase your involvement in extracurricular activities, volunteer work, and leadership roles in your application.
Need-Based Financial Aid
Some universities provide need-based financial aid to international students, though this is less common than merit-based scholarships, especially at the undergraduate level. This aid is based on the student's and their family's demonstrated financial need. Consider these points:
- Identify need-aware vs. need-blind institutions: "Need-blind" institutions do not consider an applicant's financial situation when making admissions decisions, and they commit to meeting the full demonstrated need of admitted students. However, very few US universities are need-blind for international students. "Need-aware" institutions consider the applicant's ability to pay.
- Complete the required financial aid application: You'll likely need to complete the CSS Profile and potentially submit other financial documents to verify your family's income and assets.
- Be prepared to provide documentation: Accurate and complete financial documentation is critical for need-based aid consideration.
External Scholarships and Grants
Numerous organizations and foundations offer scholarships and grants specifically for international students studying in the US. This is a crucial area to focus your search. Remember:
- Utilize online scholarship databases: Websites like Scholarships.com, InternationalStudent.com, and EducationUSA offer comprehensive lists of scholarships for international students.
- Target scholarships related to your field of study: Many professional organizations and foundations offer scholarships to students pursuing specific academic disciplines.
- Apply to as many scholarships as possible: The more scholarships you apply for, the higher your chances of receiving funding.
Graduate Assistantships and Fellowships
If you are pursuing a graduate degree (Master's or PhD), graduate assistantships and fellowships can provide substantial funding. Generally, these positions involve working as a teaching assistant (TA) or research assistant (RA). Key aspects include:
- Research faculty and departments thoroughly: Identify professors whose research interests align with yours and contact them to express your interest in working with them.
- Demonstrate strong research skills: Highlight your research experience, publications, and presentations in your application.
- Be prepared for a competitive application process: Graduate assistantships and fellowships are highly competitive, so a strong academic record and relevant experience are essential.
Tuition Waivers and Discounts
Some universities offer tuition waivers or discounts to international students in specific circumstances, such as those from partner institutions or those participating in exchange programs. Consider these options:
- Explore exchange programs: If your home university has an exchange agreement with a US university, you may be able to study in the US for a semester or year at a reduced tuition rate.
- Inquire about tuition waiver programs: Contact the international student office at the universities you are interested in to inquire about any tuition waiver programs that may be available.
- Look for "sister city" relationships: Some cities have partnerships with international cities, which can sometimes lead to educational opportunities and financial aid.
Where is tuition free for international students?

Countries Historically Known for Tuition-Free or Very Low Tuition
Historically, several European countries have offered tuition-free higher education to international students, or have had very low tuition fees. However, keep in mind that these policies can change, and often apply only to specific programs or require certain conditions.
- Germany: Germany has been a popular destination due to its generally low tuition fees for both domestic and international students, but this is not universally applicable. Some states have reintroduced tuition fees for non-EU students. You need to factor in semester fees, which cover administrative costs and student services. These fees vary, and they may include a public transport ticket.
- Norway: Norway's public universities used to offer tuition-free education for all students, regardless of nationality. However, you need to demonstrate sufficient funds for living expenses. Also, specialized programs may still charge fees.
- Iceland: Public universities in Iceland generally do not charge tuition fees, but a registration fee typically applies. As with other countries, sufficient funds for living expenses are crucial.
Understanding "Tuition-Free" - Hidden Costs
The phrase "tuition-free" can be misleading. While you might not be paying for the courses themselves, several costs need to be considered. These costs can significantly impact your overall budget.
- Semester Fees: Most universities, even those considered "tuition-free", will charge a semester fee. This fee covers administrative costs, student services, and often a public transportation ticket. The amount can vary widely.
- Living Expenses: Housing, food, transportation, and personal expenses are significant costs. Tuition-free does not equate to free living. You'll need to demonstrate financial resources to cover these expenses to obtain a student visa.
- Health Insurance: Health insurance is typically mandatory for international students. The cost of health insurance needs to be factored into your budget.
Eligibility Requirements and Restrictions
Even in countries where tuition-free education is offered, there are often specific eligibility requirements and restrictions that international students need to meet. These requirements can vary based on nationality, program of study, and level of education.
- Nationality Restrictions: Some tuition-free programs are only available to students from specific countries or regions. EU/EEA citizens often have more favorable conditions than non-EU/EEA citizens.
- Program Restrictions: Certain programs, especially postgraduate or specialized courses, may charge tuition fees even if undergraduate programs are tuition-free. Check with the university directly.
- Language Proficiency: Many programs require proof of language proficiency in the language of instruction. If you need to take language courses, this can add to your overall cost.
How to Find Tuition-Free Programs
Finding tuition-free programs requires careful research and verification. University websites, government websites, and education portals are valuable resources. Remember that information can change, so always confirm with the university.
- University Websites: The most reliable source of information is the official website of the university you are interested in. Look for international student information or fees and funding sections.
- Government Websites: Education ministries and government websites often provide information about tuition policies and scholarships.
- Education Portals: Websites like DAAD (for Germany) or Study in Norway can provide a good overview of opportunities.
The Future of Tuition-Free Education
The landscape of tuition-free education is constantly evolving. Economic pressures and policy changes can lead to the introduction or reintroduction of tuition fees. Staying informed about the latest developments is crucial.
- Policy Changes: Keep an eye on news and announcements from government and educational institutions. Tuition policies can change with little notice.
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions can influence tuition policies. Funding cuts or budget constraints may lead to increased fees.
- Stay Updated: Regularly check the websites of universities and government agencies to ensure you have the most up-to-date information.
What is the cheapest country to study for international students?
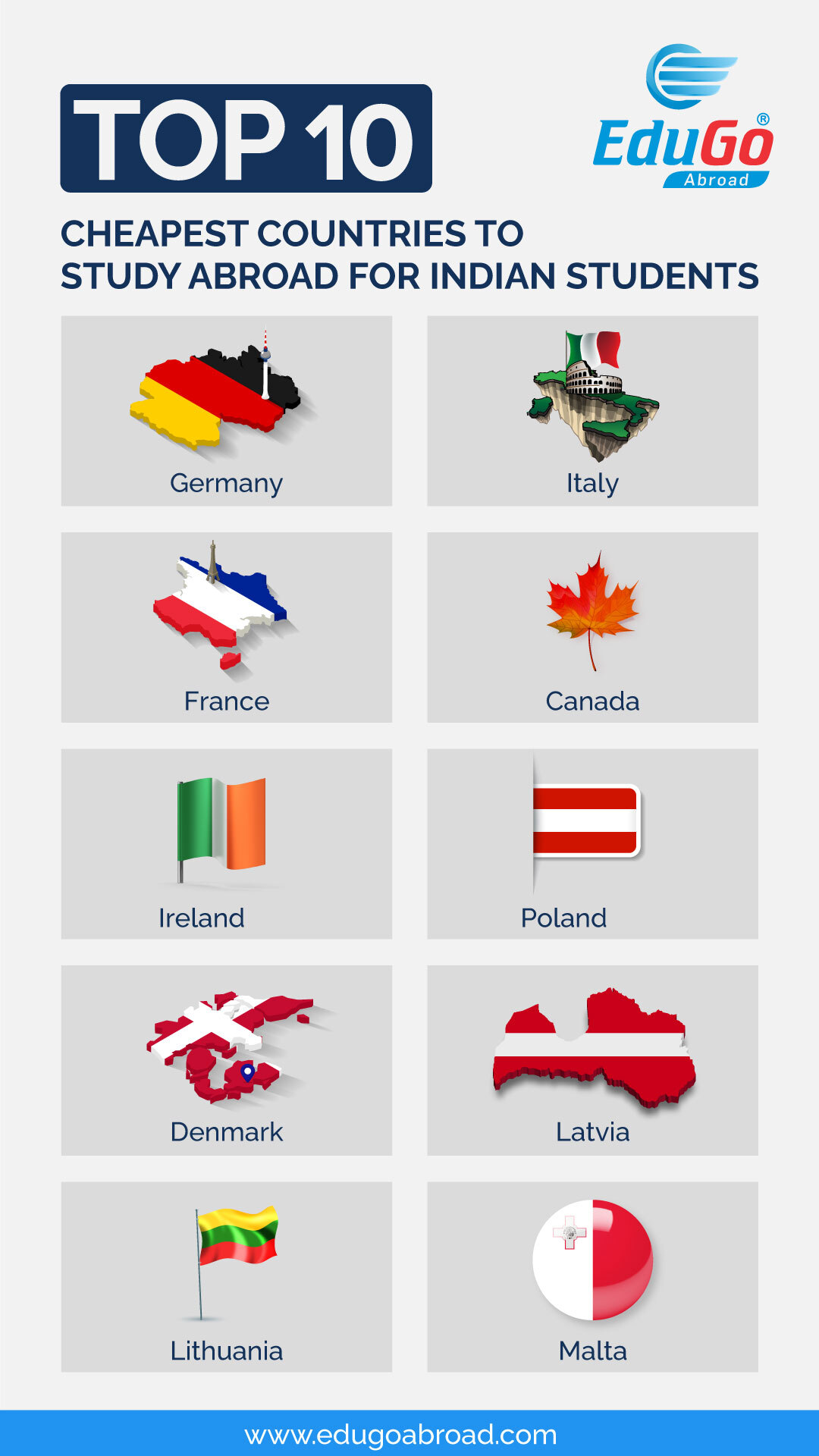
Affordable Tuition Fees: Where to Find Them
Many countries offer significantly reduced or even free tuition fees to international students at public universities. Germany and Norway are prime examples, providing tuition-free education to all students, regardless of nationality. Eastern European countries like Poland and the Czech Republic also have lower tuition costs compared to Western European nations. The cost of tuition is obviously a large part of the expense, so finding a place where this is reduced will make a big difference.
- Research public universities in European countries.
- Consider universities in Eastern Europe for lower tuition.
- Look for scholarships and grants to offset tuition fees.
Cost of Living: The Daily Grind
The cost of living, encompassing accommodation, food, transportation, and personal expenses, plays a significant role in the overall affordability of studying abroad. Countries like India, Mexico, and Argentina boast significantly lower living expenses compared to Western Europe or North America. Consider this aspect closely when evaluating your study abroad options. Finding the correct location with the right expenses can make the difference in deciding where to go.
- Estimate monthly living expenses in different countries.
- Compare accommodation costs and availability.
- Consider your lifestyle and spending habits.
Scholarships and Financial Aid: Your Funding Options
Numerous scholarships and financial aid programs are available to international students, helping to alleviate the financial burden of studying abroad. These can range from full scholarships covering tuition and living expenses to partial scholarships targeting specific fields of study or nationalities. Research and apply for as many relevant scholarships as possible to maximize your funding opportunities.
- Research scholarships offered by universities, governments, and organizations.
- Meet the eligibility criteria and application deadlines.
- Prepare a strong scholarship application showcasing your academic achievements and goals.
Currency Exchange Rates: Understanding the Impact
Currency exchange rates can significantly impact the affordability of studying abroad. A strong home currency against the currency of your host country can make education more affordable. Monitor exchange rates and plan your finances accordingly. Exchange rates can greatly affect the overall affordability depending on your home currency.
- Monitor exchange rates between your home currency and the currency of your desired country.
- Consider transferring funds when exchange rates are favorable.
- Be aware of potential fluctuations in exchange rates.
Visa Requirements and Other Associated Costs: Planning Ahead
Remember to factor in visa application fees, health insurance costs, and other associated expenses when budgeting for studying abroad. Visa requirements and healthcare costs can vary significantly between countries, so thoroughly research these aspects before making a decision. Plan for these costs as you decide where you want to study abroad.
- Research visa requirements and application fees.
- Inquire about mandatory health insurance for international students.
- Factor in travel expenses and other miscellaneous costs.
Frequently asked questions
Where can international students realistically study for free in 2025?
While truly "free" education is rare, some countries offer tuition-free or very low-cost higher education to international students. Look into Germany, known for its public universities charging minimal fees, and Norway, where public universities generally don't charge tuition, regardless of nationality. Be aware that these options usually come with living expenses and specific admission requirements, including language proficiency. Consider smaller EU countries like Finland or Sweden as well since they can be available to international students with no tuition.
What are the main criteria for international students to study for free?
The primary criteria often revolve around academic merit, language proficiency, and meeting admission requirements set by the university and the country. Many countries offering low-cost education require proficiency in their native language (e.g., German in Germany) or demonstrate strong English skills. Students must also meet the academic qualifications for their chosen program and often need to prove sufficient funds to cover living expenses, even if tuition is free. It's important to be eligible for a student visa.
What scholarships or grants can international students apply for to cover living costs?
Numerous scholarships and grants are available to help international students cover living expenses. These can be offered by the host country's government, international organizations, or individual universities. DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service) is a prominent example for Germany, while other countries have similar programs. Research privately funded scholarships that align with your field of study and nationality. A strong application is essential for receiving these competitive aids.
What are the potential drawbacks or hidden costs associated with tuition-free education abroad?
Even with tuition-free education, significant living expenses remain, including housing, food, transportation, and health insurance. Some universities charge semester fees for administrative costs and student services. Obtaining a student visa and complying with immigration regulations can involve costs and paperwork. Competition for accommodation can be fierce and expensive in popular student cities. Finally, language barriers can make it difficult to adjust and integrate into a new country, even with English-taught programs.
