Visa Tips for International Scholarship Holders

Securing an international scholarship is a significant achievement, opening doors to incredible educational opportunities. However, navigating the visa application process can feel daunting, even after receiving acceptance. This article aims to demystify the process, providing essential visa tips specifically tailored for international scholarship holders. From understanding different visa categories to gathering the necessary documentation and acing the interview, we’ll cover crucial aspects that can significantly increase your chances of a successful application. We'll help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure a smoother transition into your academic journey abroad.
Visa Tips for International Scholarship Holders
Navigating the visa application process can be daunting, especially for international students on scholarships. Securing a visa is crucial for pursuing your academic goals abroad. The key is to be meticulous and proactive. Start by thoroughly researching the specific visa requirements for your chosen country and student status. Gather all necessary documents well in advance, paying close attention to detail and ensuring accuracy. Understand the financial requirements, even if you have a scholarship, as you may need to prove sufficient funds for living expenses not covered by your scholarship. Be prepared for the interview, practice answering common questions, and present yourself confidently and respectfully. Remember, the embassy or consulate is looking to ensure you are a genuine student intending to return to your home country upon completion of your studies.
Gather Required Documents Early
The foundation of a successful visa application lies in having all the necessary documents prepared well in advance. This includes your passport (valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay), acceptance letter from the university, scholarship award letter (clearly stating the amount and duration), proof of financial resources (bank statements, sponsor letters), academic transcripts, and standardized test scores (if required). Do not wait until the last minute to collect these documents, as some may take time to obtain or translate. Having everything organized in a binder or folder can streamline the application process and demonstrate your preparedness.
Understand Financial Requirements
Even with a full scholarship, many countries require international students to demonstrate they have sufficient funds to cover living expenses, health insurance, and other miscellaneous costs not covered by the scholarship. This might involve providing bank statements, sponsorship letters, or a combination of both. Be aware of the specific financial threshold required by the embassy or consulate and ensure your documentation clearly demonstrates you meet or exceed this requirement. Include detailed information about your scholarship coverage, specifying what expenses are covered and for how long.
Prepare for the Visa Interview
The visa interview is a crucial step in the application process. While not all applicants are required to attend an interview, it's wise to be prepared. Research common visa interview questions and practice your answers beforehand. Be honest, concise, and confident in your responses. Dress professionally and arrive on time for your interview. Demonstrate a clear understanding of your study program, your academic goals, and your intentions to return to your home country after completing your studies.
Maintain Clear Communication with the University
Your university is a valuable resource throughout the visa application process. Keep them informed of your progress and any challenges you encounter. They can provide guidance, support, and documentation as needed. Your university's international student office often has experience with visa applications and can offer tailored advice based on your specific circumstances. Don't hesitate to reach out to them for assistance.
Be Aware of Visa Processing Times
Visa processing times can vary significantly depending on the country, the type of visa, and the time of year. Apply for your visa well in advance of your intended departure date to avoid any last-minute stress or delays. Check the embassy or consulate website for estimated processing times and factor in potential delays due to holidays or unforeseen circumstances. Regularly monitor your application status and respond promptly to any requests for additional information.
| Aspect | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation | Complete and accurate documents are required. | High |
| Financial Proof | Demonstrate sufficient funds for expenses not covered by the scholarship. | High |
| Interview Preparation | Practice answering common visa interview questions. | Medium |
| University Communication | Maintain contact with the university's international student office. | Medium |
| Processing Time Awareness | Apply early and monitor your application status. | High |
How can I increase my chances of getting a U.S. tourist visa?

Understanding the Importance of "Ties to Home Country"
Strong ties to your home country are paramount. Consular officers are primarily concerned that applicants will overstay their visa and remain in the U.S. illegally. You must demonstrate that you have compelling reasons to return home.
- Evidence of employment or business ownership: Offer a letter from your employer or business registration documents.
- Family responsibilities: Marriage certificates and birth certificates of children dependent on you demonstrate family ties.
- Property ownership: Real estate deeds or mortgage statements prove significant assets in your home country.
Demonstrating Financial Stability and Support
You need to show you can afford the trip and have a reason to return, and wont stay in the U.S. to find work. Insufficient funds can lead to denial.
- Bank statements: Provide statements showing a consistent balance sufficient for your travel expenses.
- Investment records: Include investment portfolios, retirement accounts, or other financial holdings.
- Sponsorship (if applicable): If someone is sponsoring your trip, provide their financial documents and a letter of support.
Providing a Detailed and Credible Travel Itinerary
A vague or inconsistent itinerary raises suspicion. A well-planned itinerary shows you've thought about your trip and have a clear plan.
- Specific activities and destinations: List the places you plan to visit and the activities you intend to engage in.
- Dates of travel: Clearly state your arrival and departure dates.
- Accommodation arrangements: Include hotel reservations or confirmation from your host.
Preparing for the Visa Interview: What to Expect
The interview is your chance to convince the consular officer of your intentions. Answer honestly and professionally.
- Be truthful and consistent: Ensure your answers align with your application and supporting documents.
- Answer concisely and directly: Avoid rambling or providing unnecessary information.
- Dress professionally and be polite: First impressions matter.
Addressing Previous Visa Denials or Immigration Issues
Previous denials don't automatically disqualify you, but you need to address them honestly.
- Disclose previous denials: Be upfront about any previous visa denials or immigration issues.
- Explain the reasons for the previous denial: Provide a clear and honest explanation of why the visa was previously denied.
- Demonstrate changes in circumstances: Show how your situation has changed since the previous denial.
Who can sponsor an international student in the USA?

Individuals: Family and Friends
- Family members, such as parents, siblings, or grandparents, can provide financial support. The student must provide bank statements and letters of support demonstrating the availability of these funds.
- Close friends might also offer financial assistance, but this is less common and may require more documentation to prove the legitimacy of the support.
- It's crucial to note that the financial supporter must demonstrate a stable and verifiable source of income.
Educational Institutions: Scholarships and Assistantships
- Universities and colleges frequently offer scholarships based on academic merit, athletic ability, or specific fields of study. These scholarships can cover tuition, fees, and sometimes living expenses.
- Graduate students may be eligible for assistantships (teaching or research) that provide a stipend and tuition remission in exchange for their services.
- Institutional grants, which are need-based, are also available at some universities.
Governmental and Non-Governmental Organizations
- Various governments, both the student's home country and the U.S. government, may offer scholarships or grants for international students. Examples include Fulbright scholarships and specific country-based scholarships.
- Private foundations and organizations, such as the Ford Foundation or the Rotary Foundation, provide scholarships and grants in specific fields. These are often highly competitive.
- Students should research opportunities provided by organizations focused on their field of study or country of origin.
Student's Own Funds and Personal Loans
- Students can use their own savings or investments to fund their studies. They must provide bank statements showing sufficient funds.
- Some international students may be able to obtain personal loans from banks or financial institutions in their home country. However, securing loans in the U.S. as an international student can be difficult.
- Demonstrating a history of responsible financial management can increase the chances of loan approval.
Combination of Funding Sources
- It is common for international students to utilize a combination of funding sources. For example, they might receive a partial scholarship from the university and supplement it with funds from their family.
- The I-20 form, which is required for the student visa, will specify the total estimated cost of attendance and the sources of funding. This form is critical for the visa application process.
- Students must clearly document all funding sources and provide supporting evidence.
What is the best visa for international students?
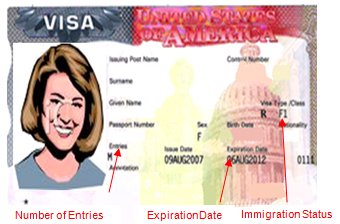
Eligibility for F-1 Visa
The F-1 visa has specific eligibility requirements that applicants must meet. This includes acceptance into a Student and Exchange Visitor Program (SEVP)-certified school or program. Students must demonstrate bona fide intent to pursue academic studies, possess sufficient financial resources to cover their expenses, and intend to return to their home country after completing their studies. Students applying for an F-1 visa are required to demonstrate their academic intention, be proficient in English, and have a residence abroad that they have no intention of abandoning.
- Acceptance into a SEVP-certified school: This is the first and foremost requirement.
- Demonstrating Financial Stability: You must prove you have the means to cover tuition, living expenses, and other costs.
- Intent to Return Home: While not explicitly stated, demonstrating ties to your home country will strengthen your application.
Benefits of the F-1 Visa
The F-1 visa offers numerous benefits to international students. It allows them to study full-time at a U.S. educational institution, work on-campus, and potentially participate in off-campus employment programs such as Optional Practical Training (OPT) and Curricular Practical Training (CPT). The F-1 visa is a non-immigrant visa that allows foreigners to pursue academic studies in the United States. Students will be able to live in the U.S. for the duration of their studies. The F-1 visa holder can also bring their spouse and children to the U.S. on an F-2 visa.
- Full-time Study: Enables students to enroll in a full course load.
- On-Campus Employment: Allows for work opportunities within the university.
- OPT/CPT Opportunities: Provides pathways for practical work experience related to the field of study.
Limitations of the F-1 Visa
Despite its advantages, the F-1 visa has certain limitations. Students are restricted to studying at the institution that issued their I-20 form (Certificate of Eligibility for Nonimmigrant Student Status). Also, they must maintain a full course load to maintain their visa status. Furthermore, off-campus work opportunities are limited and require authorization from the Designated School Official (DSO) and U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). F-1 students must strictly adhere to the terms and conditions of their visa to avoid potential deportation. The F-1 visa has limitations in regards to the amount of hours you are able to work.
- Institution-Specific: Tied to a specific school.
- Full-Time Study Requirement: Maintaining a full course load is crucial.
- Limited Off-Campus Work: Requires specific authorization and is tied to the field of study.
Alternatives to the F-1 Visa: The J-1 Visa
While the F-1 visa is most common, the J-1 Exchange Visitor visa offers an alternative for students participating in specific exchange programs. The J-1 visa is designed for individuals participating in educational and cultural exchange programs. It is often used by students participating in short-term exchange programs or those sponsored by specific organizations. However, the J-1 visa may have a two-year home-country residency requirement, meaning that after completing the program, the individual must return to their home country for at least two years before being eligible for certain other visas or green card applications.
- Exchange Programs: Specifically tailored for exchange students.
- Sponsorship: Often requires sponsorship from an organization.
- Two-Year Home Residency: A potential requirement to return home for two years.
Application Process for the F-1 Visa
The F-1 visa application process involves several key steps. First, the student must apply to and be accepted by an SEVP-certified school. Once accepted, the school will issue an I-20 form. Next, the student must pay the Student and Exchange Visitor Information System (SEVIS) fee and schedule an interview at a U.S. embassy or consulate. During the interview, the applicant will be required to provide documentation demonstrating their eligibility for the visa, including their I-20 form, proof of financial resources, and evidence of their intent to return to their home country after completing their studies. The application process also requires filling out the DS-160 form.
- School Acceptance and I-20: Getting accepted and receiving the I-20 are crucial first steps.
- SEVIS Fee Payment: Required payment for the SEVIS system.
- Consular Interview: A mandatory interview at a U.S. embassy or consulate.
Which country has highest visa success rate for international students?

Visa Application Factors
- Country of Origin: The applicant's nationality significantly influences the visa approval rate. Some countries are considered "low-risk" due to various socio-economic factors and a history of visa compliance among their citizens. Applicants from these countries often experience higher approval rates.
- Field of Study: Certain fields of study, particularly those considered crucial for the host country's economy (e.g., STEM fields - Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics), may receive preferential treatment in visa processing.
- Financial Resources: Demonstrating sufficient financial resources to cover tuition fees, living expenses, and other related costs is a critical factor. Applicants must provide evidence of their ability to support themselves financially throughout their studies.
Canada's Approach to International Students
- Streamlined Visa Process: Canada has implemented various programs to streamline the visa application process for international students, such as the Student Direct Stream (SDS) for eligible countries.
- Immigration Pathways: Canada offers numerous pathways to permanent residency for international students after graduation, making it an attractive destination for those seeking long-term opportunities.
- Emphasis on Education: The Canadian government and universities actively promote Canada as a welcoming and supportive environment for international students, contributing to a positive perception and potentially higher approval rates.
Germany's Education System and Visa Policies
- Tuition-Free Education: Germany offers tuition-free education at public universities for both domestic and international students, making it a highly appealing option. While there are semester fees to pay, tuition being free drastically cuts costs and makes the country attractive.
- Clear Visa Requirements: The German embassy or consulate provides clear and detailed information about the visa requirements, making the application process more transparent and manageable.
- Strong Economy: Germany's strong economy and demand for skilled workers make it an attractive destination for international students seeking employment opportunities after graduation.
Australia's Points-Based System
- Simplified Student Visa Framework: Australia has implemented a simplified student visa framework to streamline the application process and reduce processing times.
- Quality Education System: Australian universities are highly ranked globally, attracting students from around the world.
- Post-Study Work Opportunities: Australia offers various post-study work visas, allowing international graduates to gain valuable work experience in the country.
Data Limitations and Considerations
- Lack of Publicly Available Data: Comprehensive and up-to-date data on visa success rates for all countries is often not publicly available, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions.
- Fluctuations in Approval Rates: Visa approval rates can fluctuate based on various factors, including changes in immigration policies, economic conditions, and geopolitical events.
- Individual Circumstances: Each visa application is assessed individually, and the outcome depends on the applicant's specific circumstances and the quality of their application.
Frequently asked questions
What are the essential documents needed when applying for a visa as an international scholarship holder?
Essential documents typically include your passport, acceptance letter from the university, the scholarship award letter clearly stating the funding amount and duration, proof of sufficient funds (if required in addition to the scholarship), a visa application form, passport-sized photographs, and any other documents specifically requested by the embassy or consulate of the country where you intend to study; it's critical to meticulously review the embassy's requirements to prevent delays.
How can I demonstrate 'ties to home country' to ensure visa approval as a scholarship recipient?
Demonstrating strong 'ties to home country' is vital to alleviate concerns about overstaying your visa; This can be achieved by providing evidence such as property ownership, family responsibilities, job offers upon graduation, or significant investments in your home country, all of which showcase your intention to return after completing your studies; a well-articulated statement of purpose outlining your career goals and how your studies will benefit your home country is also highly beneficial.
What should I do if my visa application is rejected even with a scholarship?
If your visa application is rejected, first, request a written explanation from the embassy or consulate outlining the reasons for the denial; thoroughly review these reasons and gather any additional documentation that addresses their concerns; you may be able to appeal the decision or reapply with stronger evidence to support your case, potentially seeking guidance from your university's international student office or an immigration attorney.
Are there specific visa categories for international students with scholarships, and how do I determine which one to apply for?
While the specific names may vary by country, most countries have a designated student visa category (e.g., F-1 in the US, Tier 4 in the UK) specifically designed for individuals pursuing academic studies; your university's admission or international student office will typically provide guidance on the appropriate visa category for your scholarship program and will often assist you in navigating the application process; clarifying this early on is vital to avoid applying for the wrong type of visa.
