The Ultimate Guide to Higher Education Funding

Navigating the world of higher education funding can feel like traversing a complex maze. Rising tuition costs often create a significant barrier for students aspiring to pursue their academic dreams. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the funding landscape, providing invaluable insights into various avenues for financing your education. From scholarships and grants to loans and work-study programs, we explore diverse options, empowering you to make informed decisions and alleviate the financial burden associated with higher education. Discover strategies to maximize your eligibility, effectively manage your finances, and unlock the doors to a brighter future.
Funding Your Future: A Comprehensive Guide to Higher Education Finance
Navigating the world of higher education funding can seem daunting, but understanding the available options and strategies is crucial for making informed decisions about your future. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various avenues for financing your education, from federal and state aid to scholarships, grants, and loans. By exploring these resources and developing a smart financial plan, you can minimize debt and achieve your academic goals. It’s essential to start the process early, thoroughly research each option, and carefully consider your financial situation to make the best choices for your individual circumstances. Careful planning can make higher education accessible and affordable.
Understanding Federal Student Aid: FAFSA and Eligibility
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the cornerstone of federal financial aid. Completing the FAFSA is the first step to accessing grants, loans, and work-study programs offered by the U.S. Department of Education. Your eligibility for these programs is determined by your Expected Family Contribution (EFC), which is calculated based on your family's income, assets, and other factors. Understanding how the FAFSA works and accurately completing the application is vital to maximizing your potential aid package. Meeting deadlines is also crucial, as funding is often limited.
Exploring Scholarship Opportunities: Finding and Applying
Scholarships are "free money" that you don't have to repay, making them an incredibly valuable resource for funding your education. Numerous scholarship opportunities exist, offered by universities, private organizations, corporations, and even individuals. Thoroughly research scholarships that align with your academic interests, extracurricular activities, background, and demographics. Crafting compelling applications that highlight your achievements, skills, and goals is essential for standing out from the competition. Dedicate time and effort to the scholarship application process to significantly reduce your reliance on loans.
Understanding Student Loans: Federal vs. Private
Student loans can be a necessary tool for financing higher education, but it's important to understand the different types of loans available and their terms. Federal student loans generally offer lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options compared to private loans. Private loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks and other financial institutions and may have variable interest rates and less borrower protection. Carefully compare the terms of both federal and private loans, including interest rates, repayment plans, and potential fees, to choose the option that best fits your financial situation and minimizes your long-term debt burden.
Creating a Budget and Managing Student Debt
Creating a budget is essential for managing your finances during college and after graduation. Tracking your income and expenses will help you identify areas where you can save money and avoid unnecessary debt. When managing student debt, consider income-driven repayment plans, which can adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. Explore options for loan forgiveness or cancellation if you qualify. Developing a responsible financial plan and sticking to it will help you avoid financial stress and ensure you can repay your loans comfortably. Prioritizing financial literacy is a key aspect of successful debt management.
The Role of Grants: Pell Grants and State Funding
Grants are another form of "free money" that you don't have to repay, and they can significantly reduce the overall cost of your education. The Pell Grant is a federal grant awarded to undergraduate students with exceptional financial need. State governments also offer grants to residents attending colleges and universities within their state. Researching and applying for both federal and state grants can provide substantial financial assistance. Meeting the eligibility requirements and application deadlines is crucial to maximizing your chances of receiving these valuable resources.
| Funding Source | Description | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) | Grants, loans, work-study programs | Lower interest rates, flexible repayment options | Requires completion of FAFSA, eligibility based on EFC |
| Scholarships | "Free money" awarded based on merit or need | Reduces reliance on loans, no repayment required | Competitive application process, requires research |
| Grants (Pell, State) | "Free money" awarded based on financial need | No repayment required, can significantly reduce tuition costs | Eligibility requirements, application deadlines |
| Federal Student Loans | Loans provided by the U.S. Department of Education | Lower interest rates, flexible repayment plans | Requires repayment, accrues interest |
| Private Student Loans | Loans provided by banks and financial institutions | May offer higher loan amounts | Potentially higher interest rates, less flexible repayment |
What can you use FAFSA money for?

Tuition and Fees
FAFSA money is first and foremost designed to cover tuition and mandatory fees charged by your school. This includes the cost of instruction, access to facilities, and other required fees for enrollment. If you have remaining funds after covering these costs, you can use them for other educational expenses.
- Tuition: Covering the cost of classes and instruction.
- Mandatory Fees: Covering fees required for enrollment, such as student activity fees, technology fees, or health service fees.
- Lab Fees: Fees associated with specific courses that require specialized equipment or materials.
Room and Board
FAFSA funds can be used to cover the cost of room and board, whether you live on campus or off campus. If you live on campus, this includes the cost of your dorm room and meal plan. If you live off campus, it can help cover rent and food expenses. The amount you can use for housing depends on your school's cost of attendance calculations.
- On-Campus Housing: Covers the cost of dormitories or other university-provided housing.
- Meal Plans: Covers the cost of meals provided by the university.
- Off-Campus Housing: Covers rent, utilities, and groceries for students living independently.
Books and Supplies
A significant portion of FAFSA aid can be allocated towards books, supplies, and equipment needed for your courses. This includes textbooks, notebooks, pens, calculators, and any other necessary materials. Schools may factor in the estimated cost of these items into the overall cost of attendance.
- Textbooks: Covers the cost of required reading materials for courses.
- School Supplies: Covers the cost of notebooks, pens, and other necessary stationery.
- Course-Related Equipment: Covers the cost of specialized equipment needed for specific courses, such as art supplies, lab coats, or software.
Transportation
FAFSA funds can also be used to cover transportation costs associated with attending school. This can include expenses for commuting to campus, such as gas, public transportation fares, or parking fees. Some institutions may include an allowance for transportation in their cost of attendance calculations.
- Commuting Expenses: Covers the cost of driving to and from campus, including gas, tolls, and parking.
- Public Transportation: Covers the cost of bus, train, or subway fares for commuting.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Covers maintenance of car if needed to go to school
Other Educational Expenses
In addition to the core expenses mentioned above, FAFSA money can sometimes be used for other education-related costs deemed necessary by the school. This might include childcare expenses (if you are a parent), costs associated with a disability, or other unique educational needs. Always check with your school's financial aid office to confirm what expenses are covered.
- Childcare Expenses: Covers childcare costs that enable you to attend classes.
- Disability-Related Expenses: Covers expenses related to accommodations or assistive technology for students with disabilities.
- Professional Certifications: Covers cost of certifications in your area of study
What is higher education funding?
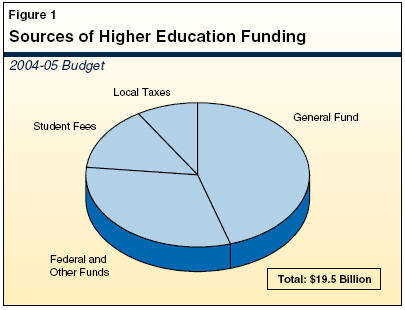
Tuition and Fees
Tuition and fees paid by students are a significant source of revenue for many higher education institutions.
The level of tuition can vary widely depending on the type of institution (public vs. private), the program of study, and the student's residency status.
Institutions often use tuition revenue to cover instructional costs, student services, and administrative expenses.
- Impact on Accessibility: Higher tuition can create barriers to access for students from low-income backgrounds.
- Funding Models: Some institutions rely more heavily on tuition revenue than others, impacting affordability.
- Financial Aid: The availability of financial aid is crucial for mitigating the impact of tuition costs on students.
Government Funding
Government funding, both at the state and federal levels, plays a crucial role in supporting higher education.
This funding can come in the form of direct appropriations to institutions, grants for specific programs or research projects, and financial aid for students.
Government support is often intended to promote access, affordability, and quality in higher education.
- State Appropriations: Direct funding from state governments is a key source of support for public colleges and universities.
- Federal Grants: Federal agencies, such as the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), provide grants for research and development.
- Student Aid Programs: Federal and state governments offer various financial aid programs, such as Pell Grants and subsidized loans, to help students afford college.
Philanthropy and Private Giving
Philanthropic donations from alumni, corporations, foundations, and other private donors can provide substantial support for higher education institutions.
These gifts can be used to fund scholarships, endow professorships, build new facilities, and support research initiatives.
Philanthropy plays a particularly important role in supplementing other funding sources and enabling institutions to pursue innovative projects.
- Endowments: Large donations are often invested to create endowments, which provide a steady stream of income for institutions.
- Capital Campaigns: Institutions frequently launch capital campaigns to raise large sums of money for specific projects or initiatives.
- Alumni Giving: Cultivating relationships with alumni is crucial for encouraging continued philanthropic support.
Research Grants and Contracts
Research grants and contracts are a significant source of funding for universities, particularly those with strong research programs.
These funds are typically awarded by government agencies, private foundations, and corporations to support specific research projects.
Research funding not only advances knowledge but also contributes to the economic development of the surrounding community.
- Federal Funding Agencies: Agencies like NIH, NSF, and the Department of Defense are major providers of research grants.
- Industry Partnerships: Universities often collaborate with private companies to conduct research that benefits both parties.
- Indirect Costs: A portion of research grants is typically allocated to cover the indirect costs of conducting research, such as facilities and administrative support.
Auxiliary Enterprises and Other Revenue Sources
In addition to tuition, government funding, and philanthropy, higher education institutions generate revenue from a variety of auxiliary enterprises and other sources.
These can include revenue from housing and dining services, bookstores, athletic programs, and licensing agreements.
These revenue streams can help to offset the cost of operating the institution and providing services to students.
- Housing and Dining: Revenue from student housing and dining services can be substantial, particularly at residential colleges.
- Athletic Programs: Successful athletic programs can generate significant revenue through ticket sales, sponsorships, and merchandise.
- Investment Income: Universities often invest their endowment funds and other assets to generate income.
What is the average financial aid package?
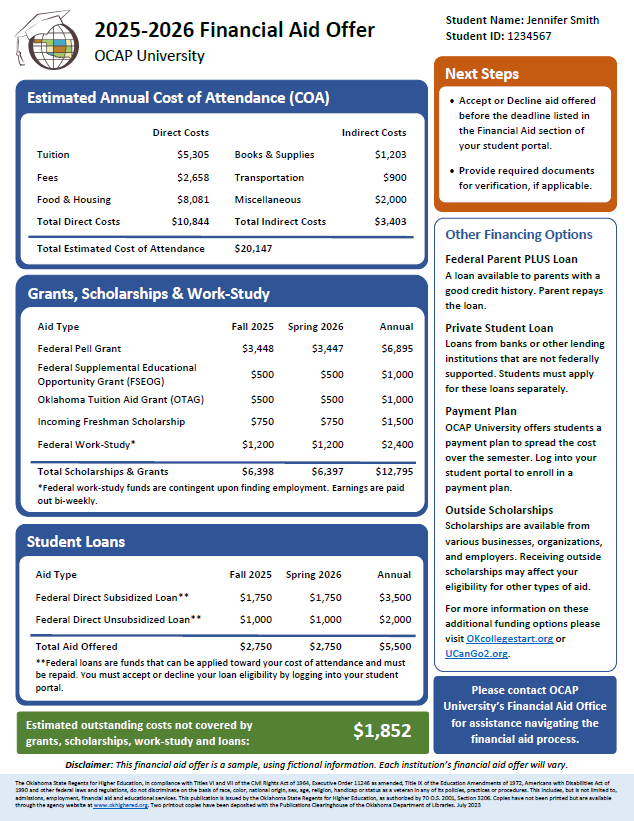
Average Financial Aid Package Breakdown
The average financial aid package is composed of several different types of aid, each contributing differently to the total amount. Understanding these components is crucial to interpreting the overall package.
- Grants: These are need-based awards that do not need to be repaid, such as the Federal Pell Grant. They often form a significant portion of the aid package for lower-income students.
- Scholarships: These are merit-based or need-based awards that also do not need to be repaid, often coming from the institution itself, private organizations, or the government.
- Federal Student Loans: These are loans offered by the federal government, typically with lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options compared to private loans. They are also a common component of financial aid packages.
- Work-Study Programs: These programs allow students to earn money through part-time employment, often on campus, to help cover educational expenses.
Factors Influencing the Average Aid Package
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the size and composition of an individual student's financial aid package. Being aware of these factors can help students and families better estimate their potential aid eligibility.
- Family Income: Generally, students from lower-income families receive larger aid packages, especially in the form of grants and scholarships. This is because financial need is a primary determinant for need-based aid.
- Cost of Attendance: The more expensive the college or university, the larger the potential aid package. However, this also often means a higher loan component, depending on the institution's endowment and commitment to need-based aid.
- Academic Merit: High-achieving students may qualify for merit-based scholarships, which can significantly increase their overall aid package, regardless of their family's income.
- Type of Institution: Private colleges and universities often have larger endowments and can offer more generous need-based aid compared to public institutions, although public schools usually have lower tuition rates overall.
Impact of Institutional Policies on Aid
Colleges and universities have their own policies and priorities when it comes to distributing financial aid. These policies can significantly influence the types and amounts of aid offered to students.
- Need-Based vs. Merit-Based Aid: Some institutions prioritize need-based aid, while others focus more on merit-based scholarships. This affects the distribution of aid among different student populations.
- Endowment Size: Institutions with larger endowments can afford to offer more generous aid packages, often reducing the reliance on student loans.
- Meeting Full Need: Some colleges pledge to meet 100% of demonstrated financial need, which means they will cover the difference between the cost of attendance and what the family can afford.
- Financial Aid Philosophy: Each institution has its own approach to awarding aid, which may emphasize minimizing student debt or attracting high-achieving students, regardless of their financial background.
Regional Variations in Average Aid
Financial aid availability and average package amounts can vary based on geographical location. This is due to differences in state funding for higher education, regional cost of living, and the prevalence of private institutions.
- State Funding for Public Institutions: States with stronger support for public colleges and universities often have lower tuition rates and may offer more substantial state-sponsored aid programs.
- Cost of Living Differences: Areas with higher cost of living may have institutions that provide larger aid packages to help students cover their expenses.
- Concentration of Private Institutions: Regions with a higher concentration of private colleges and universities may have a higher average aid package due to the greater availability of institutional aid.
- Economic Conditions: The economic health of a region can impact the amount of aid available, as states with strong economies may allocate more resources to higher education.
The Future of Financial Aid Packages
The landscape of financial aid is constantly evolving, influenced by factors such as changes in government policies, rising tuition costs, and shifts in institutional priorities. Understanding these trends can help students and families prepare for the future.
- Tuition Inflation: As tuition costs continue to rise, the pressure on financial aid systems increases, potentially leading to larger loan burdens for students.
- Government Policies: Changes in federal and state financial aid policies can significantly impact the amount and types of aid available.
- Institutional Innovation: Colleges and universities are exploring new models of financial aid, such as income-share agreements and tuition freezes, to make education more affordable.
- Focus on Affordability: There is a growing emphasis on making higher education more accessible and affordable, leading to potential reforms in financial aid systems.
Frequently asked questions
What is the primary focus of 'The Ultimate Guide to Higher Education Funding'?
The primary focus is on providing a comprehensive overview of various funding options available for higher education, including scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs. It aims to equip students and their families with the knowledge and resources necessary to navigate the complex landscape of college financing and minimize their financial burden.
Who is the intended audience for 'The Ultimate Guide to Higher Education Funding'?
This guide is primarily intended for high school students planning to attend college, current college students seeking additional funding, parents and families supporting their children's education, and guidance counselors or financial aid advisors looking for a reliable resource to assist their students. It is designed to be accessible and informative for anyone involved in the process of financing higher education.
Does 'The Ultimate Guide to Higher Education Funding' cover international student funding?
While the guide's main focus may be on funding options within a specific country (depending on the guide's origin), it often includes a section or chapter dedicated to funding opportunities for international students. This section typically covers scholarships specifically for international students, loan programs available to international students, and visa requirements related to funding and studying abroad. However, the depth of coverage on international funding will vary depending on the specific guide.
How often is 'The Ultimate Guide to Higher Education Funding' updated?
The frequency of updates varies depending on the publisher and the rapidly changing nature of financial aid. A reputable guide should be updated annually or bi-annually to reflect new scholarship programs, changes in government policies regarding grants and loans, and adjustments to eligibility criteria. Look for the publication date to ensure you are using the most current and accurate information.
