Funding Options for Low-Income Students in the USA
Securing funding for higher education can be a daunting task, especially for low-income students in the United States. The financial burden often poses a significant barrier, hindering access to valuable educational opportunities. Fortunately, a range of funding options exists to help bridge this gap and empower students from disadvantaged backgrounds to pursue their academic dreams. This article explores various avenues for financial assistance, including federal and state grants, scholarships tailored to low-income individuals, work-study programs, and loan options. By understanding these resources, students can navigate the complex landscape of college funding and unlock their potential for a brighter future.
Funding Options for Low-Income Students in the USA
Many low-income students in the USA face significant financial barriers when pursuing higher education. Fortunately, a variety of funding options exist to help alleviate these challenges. These resources range from federal and state government programs to institutional aid and private scholarships, all aimed at making college more accessible and affordable. Navigating this landscape can be complex, so understanding the available options and eligibility requirements is crucial for students seeking to finance their education. Successfully securing funding often involves meticulous planning, diligent application processes, and a comprehensive understanding of the various avenues available. The goal is to minimize debt and maximize opportunities for academic success.
Federal Grants and Aid
The Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the cornerstone of federal financial aid. The Pell Grant is a needs-based grant available to undergraduate students with exceptional financial need, and it does not need to be repaid. Students may also qualify for other federal grants like the Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (FSEOG), which is administered by participating institutions and prioritizes students with the greatest financial need. Applying for federal aid involves completing the FAFSA, which uses a formula to determine a student's Expected Family Contribution (EFC), and this figure helps determine the amount of aid a student can receive.
State-Specific Financial Aid Programs
Many states offer their own financial aid programs designed to support low-income students residing within their borders. These programs vary significantly by state, with some offering grants, scholarships, and tuition assistance based on financial need and academic merit. For example, California offers the Cal Grant, a program that provides tuition assistance to eligible students attending California colleges and universities. It's essential for students to research and understand the specific programs available in their state of residence, as eligibility criteria and application deadlines can differ considerably. These state-level aids often complement federal aid and provide substantial financial support to students pursuing higher education.
Institutional Scholarships and Grants
Colleges and universities often have their own scholarship and grant programs specifically for low-income students. These are typically funded by the institution's endowment, alumni donations, and other sources. Many institutions offer merit-based scholarships that consider academic achievement, leadership skills, and extracurricular involvement. Additionally, need-based scholarships are available for students demonstrating significant financial need. It's important for students to research the specific scholarships and grants offered by the colleges they are applying to and to meet all application requirements.
Private Scholarships and Grants
Numerous private organizations, foundations, and companies offer scholarships and grants to students from diverse backgrounds, including those from low-income families. Websites like Scholarships.com, Fastweb, and Sallie Mae's Scholarship Search provide databases of scholarships and grants that students can search based on their qualifications and interests. These scholarships can range from small awards to substantial sums that cover a significant portion of tuition and expenses. Securing private scholarships often requires a significant investment of time and effort in researching opportunities and crafting compelling applications.
Work-Study Programs and Student Loans
Federal Work-Study programs offer part-time employment opportunities for students with financial need, allowing them to earn money to help pay for their education. These jobs are typically on-campus and provide valuable work experience. Student loans, both federal and private, are another option for financing college, but they should be approached with caution. Federal student loans generally offer more favorable terms and repayment options compared to private loans. It is crucial for students to understand the terms of their loans, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and potential for deferment or forbearance, before borrowing money.
| Funding Option | Description | Eligibility | Repayment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pell Grant | Federal grant for undergraduates with exceptional financial need. | Based on FAFSA results and financial need. | Not required. |
| State Grants (e.g., Cal Grant) | State-funded grants for residents attending in-state colleges. | Varies by state; typically based on residency and financial need. | Not required. |
| Institutional Scholarships | Scholarships offered by individual colleges and universities. | Varies by institution; can be merit-based or need-based. | Not required. |
| Private Scholarships | Scholarships from private organizations and foundations. | Varies widely; may have specific criteria based on background or field of study. | Not required. |
| Federal Work-Study | Part-time employment for students with financial need. | Based on FAFSA results and financial need. | Not required. |
| Federal Student Loans | Loans provided by the federal government. | Based on FAFSA results; repayment required with interest. | Repayment required with interest. |
What are the 4 types of financial aid for students?
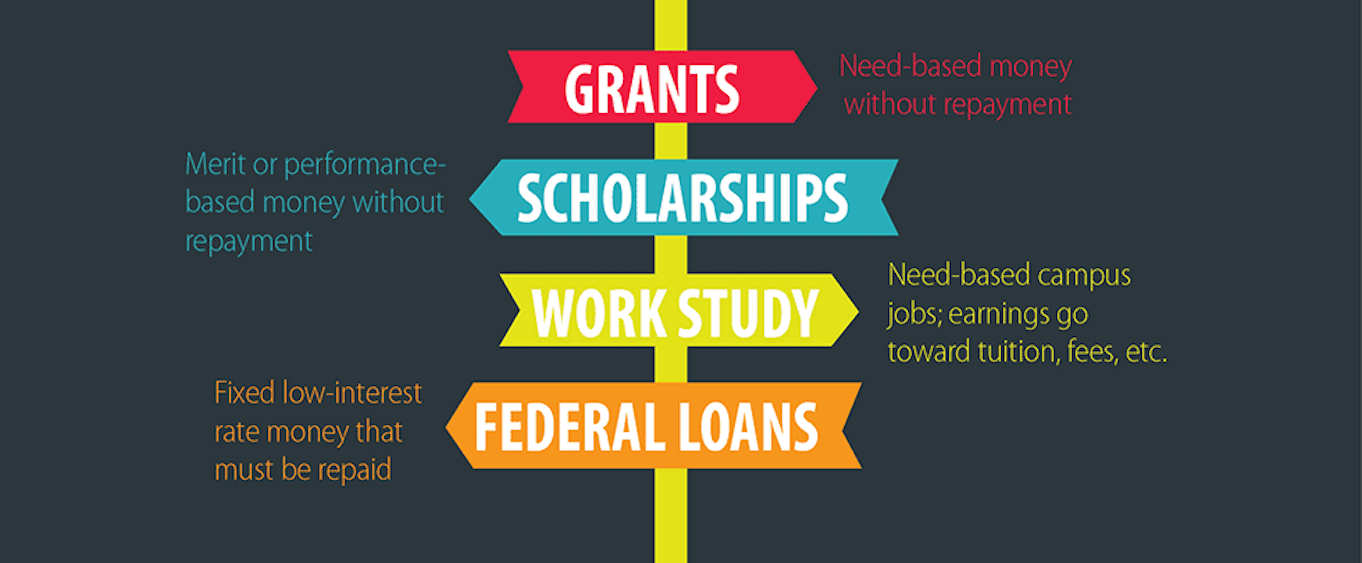
Grants
Grants are a form of financial aid that you do not have to repay, making them a highly desirable option. They are typically awarded based on financial need and can come from various sources.
- Federal Grants: These are provided by the U.S. federal government. The most well-known is the Pell Grant, which is awarded to undergraduate students with exceptional financial need.
- State Grants: Many states offer grant programs to students who attend schools within their state. Eligibility requirements vary by state.
- Institutional Grants: Colleges and universities themselves often provide grants to their students based on financial need or other criteria.
Scholarships
Scholarships, like grants, are a type of aid that does not require repayment. However, scholarships are usually awarded based on merit, talent, or specific criteria rather than solely on financial need.
- Academic Scholarships: Awarded for outstanding academic achievement.
- Athletic Scholarships: Given to students who excel in sports and are recruited to play on college teams.
- Private Scholarships: Offered by a wide range of organizations, foundations, and companies. These can have very specific eligibility requirements.
Student Loans
Student loans are a form of financial aid that must be repaid, usually with interest. They can be a necessary option for many students, but it's important to borrow responsibly and understand the terms of the loan.
- Federal Student Loans: These are offered by the U.S. Department of Education and typically have lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options than private loans. There are subsidized and unsubsidized federal loans.
- Private Student Loans: Offered by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. These may have higher interest rates and less flexible repayment options than federal loans.
- Loan Repayment Plans: Federal loans offer income-driven repayment plans to make payments affordable based on your income.
Work-Study Programs
Work-study programs provide students with the opportunity to earn money to help pay for college expenses by working part-time. These jobs are typically on-campus or with approved off-campus employers.
- Federal Work-Study: This program is funded by the federal government and is available to students who demonstrate financial need.
- Institutional Work-Study: Some colleges offer their own work-study programs.
- Benefits: Allows students to gain valuable work experience while earning money to cover educational costs.
Understanding the Application Process for Each Type
Applying for financial aid involves different processes depending on the type of aid you are seeking. It is crucial to understand these processes to maximize your chances of receiving assistance.
- FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid): This is the main application for federal student aid, including grants, loans, and work-study. It's important to complete it accurately and on time.
- Scholarship Applications: Each scholarship will have its own application process and requirements. Thoroughly research and meet all criteria.
- Institutional Aid Application: Check with the college or university's financial aid office for their specific application procedures.
Is the 6495 grant real?

Grant Program Specificity
Grant programs are almost invariably associated with a specific funding agency or organization. The program will have a clearly defined name, purpose, and eligibility requirements. Consider these key point:
- Government Grants: These are typically administered by federal, state, or local government agencies, and are usually easy to verify.
- Foundation Grants: These are offered by private foundations and often focus on specific areas such as education, arts, or social services.
- Corporate Grants: Businesses often have grant programs that support community initiatives or research related to their industry.
Warning Signs of Grant Scams
Several red flags can indicate a grant scam. Always be skeptical if:
- You are asked to pay a fee to receive the grant: Legitimate grant programs never require recipients to pay money upfront to access the funds.
- The grant offer seems too good to be true: Scammers often promise large sums of money with minimal effort.
- You are pressured to act quickly: Scammers want to rush you into making a decision before you have time to research the offer.
- The contact information is vague or unprofessional: Scammers may use generic email addresses or lack verifiable contact details.
How to Verify a Grant Offer
To verify the legitimacy of a grant offer, take the following steps:
- Identify the Granting Organization: Find the name of the organization purportedly offering the grant.
- Search for the Organization Online: Look up the organization's official website to confirm its existence and legitimacy.
- Contact the Organization Directly: Use the contact information listed on the official website to inquire about the grant program.
- Check with Relevant Government Agencies: For government grants, contact the relevant federal or state agency to verify the program.
Resources for Finding Legitimate Grants
There are many legitimate resources available for finding grant opportunities. These include:
- Grants.gov: This is the official website of the U.S. federal government for finding and applying for grants.
- Foundation Center: This organization provides information and resources on foundations and their grant programs.
- State and Local Government Websites: Many state and local governments have websites that list grant opportunities available to residents and organizations.
Protecting Yourself from Grant Fraud
Protecting yourself from grant fraud involves vigilance and caution. Key measures to take include:
- Never provide personal or financial information upfront: Legitimate grant programs will not ask for your bank account details or Social Security number before you are approved.
- Be wary of unsolicited offers: If you receive a grant offer out of the blue, be very cautious.
- Research the organization thoroughly: Before applying for any grant, verify the legitimacy of the organization offering it.
- Report suspected scams: If you believe you have been targeted by a grant scam, report it to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Does FAFSA help low income students?

FAFSA as a Needs-Based System
FAFSA operates on a needs-based system, meaning that financial aid is awarded primarily based on a student's financial need. The information you provide on the FAFSA is used to calculate your Expected Family Contribution (EFC), which is an estimate of how much your family can contribute to your education. Students with lower EFCs, typically those from low-income households, are considered to have greater financial need and are therefore eligible for more financial aid.
- Assesses the student's financial situation, including income, assets, and household size.
- Calculates an Expected Family Contribution (EFC), an estimate of what the student and their family can afford to pay.
- Determines financial need by subtracting the EFC from the Cost of Attendance (COA) at the chosen school.
Pell Grants and Low-Income Students
The Federal Pell Grant is a key source of aid for low-income students. It is a grant, which means it does not have to be repaid. Pell Grants are awarded to undergraduate students with exceptional financial need. The amount of the Pell Grant depends on the student's EFC, the cost of attendance at the school, whether the student is a full-time or part-time student, and whether the student attends for a full academic year or less. Pell Grants are typically awarded to students with the lowest EFCs.
- Specifically targeted towards undergraduate students with exceptional financial need.
- Does not require repayment, unlike student loans.
- The amount awarded depends on EFC, Cost of Attendance, and enrollment status.
Federal Student Loans and Subsidized Loans
FAFSA also unlocks access to federal student loans. Subsidized federal loans are particularly beneficial for low-income students. With subsidized loans, the government pays the interest that accrues while the student is in school, during the grace period, and during periods of deferment. This helps to keep the overall cost of borrowing down for students who might struggle to afford interest payments while also focusing on their studies.
- Subsidized loans offer interest-free periods while in school, during grace periods, and during deferment.
- Lower interest rates often associated with federal loans compared to private loans.
- Provides structured repayment options and potential for loan forgiveness programs.
Work-Study Programs and On-Campus Employment
By completing the FAFSA, low-income students may also be eligible for federal work-study programs. These programs provide part-time jobs for undergraduate and graduate students with financial need, allowing them to earn money to help pay for their education. Work-study positions are often on-campus, making it easier for students to balance work and studies.
- Offers part-time employment opportunities for students with financial need.
- Provides on-campus or off-campus employment related to the student's field of study or community service.
- Enables students to earn money while attending school, reducing reliance on loans.
State and Institutional Aid Based on FAFSA
Many states and colleges use the information from the FAFSA to determine eligibility for their own financial aid programs. These programs can include grants, scholarships, and loan programs. Therefore, completing the FAFSA is often the first step in accessing a wider range of financial aid opportunities, beyond just federal aid. State and institutional aid are important supplements to federal aid, helping to further reduce the financial burden on low-income students.
- States and colleges use FAFSA data to determine eligibility for their own aid programs.
- These programs can include grants, scholarships, and loan programs.
- Increases the total aid package available to low-income students.
Frequently asked questions
What are the primary federal financial aid options available for low-income students?
The main federal resources include the Pell Grant, which is a grant awarded based on financial need and does not need to be repaid, and federal student loans, such as Subsidized Stafford Loans, where the government pays the interest while the student is in school. Eligibility is determined through the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
Are there specific scholarships targeted towards low-income students?
Yes, many scholarships are specifically designed for students with financial need. Organizations like the United Negro College Fund (UNCF), the Hispanic Scholarship Fund (HSF), and various community foundations offer scholarships with a focus on low-income and minority students, often considering academic merit and extracurricular involvement in addition to financial circumstances.
What state-level aid programs exist for low-income students?
Many states offer their own grant and scholarship programs to supplement federal aid. These programs vary greatly by state, but often prioritize residents attending in-state public universities and colleges. Examples include the California Cal Grant and the Texas Tuition Equalization Grant. Students should research the specific programs available in their state of residency.
How can community colleges be a more affordable option for low-income students?
Community colleges generally have significantly lower tuition costs compared to four-year universities. This affordability, coupled with access to Pell Grants and other financial aid, makes them an attractive option for low-income students. Students can complete their general education requirements at a community college and then transfer to a four-year institution to complete their bachelor's degree, reducing overall costs.
